区块链的英文是 Blockchain。
Introduction to Blockchain Technology

Blockchain technology has emerged as a revolutionary force in the digital world, reshaping industries and transforming the way we perceive data security and transaction integrity. This article delves into the basics of blockchain, its working principles, and its potential impact on various sectors.
What is Blockchain?
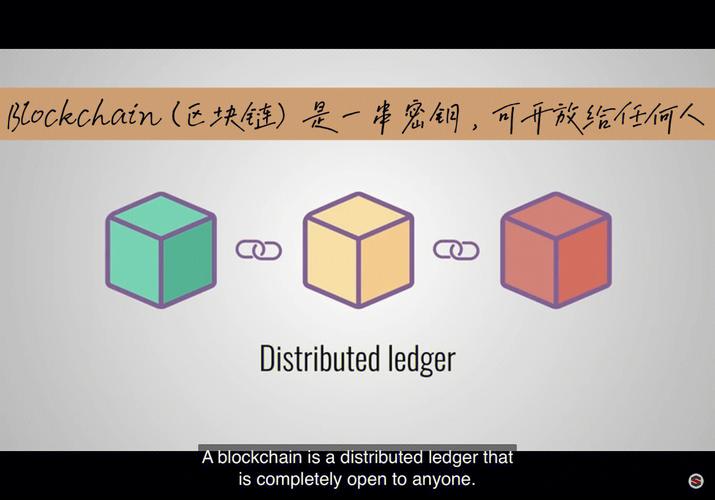
Blockchain is a decentralized digital ledger that records transactions across many computers so that the record cannot be altered retroactively without the alteration of all subsequent blocks and the consensus of the network. It is essentially a chain of blocks, where each block contains a list of transactions.
Key Features of Blockchain

There are several key features that make blockchain unique and secure:
Decentralization: Unlike traditional centralized systems, blockchain operates on a decentralized network, reducing the risk of a single point of failure.
Transparency: All transactions are recorded on the blockchain and can be viewed by anyone, ensuring transparency and accountability.
Immutability: Once a transaction is recorded on the blockchain, it cannot be altered, making it tamper-proof.
Security: Blockchain uses advanced cryptographic techniques to secure transactions and protect against hacking and fraud.
How Does Blockchain Work?
Blockchain operates through a series of interconnected steps:
Transaction: A transaction is created and broadcasted to the network.
Validation: Nodes in the network validate the transaction to ensure it meets the required criteria.
Block Creation: Once validated, the transaction is added to a new block.
Chain Formation: The new block is linked to the previous block using a cryptographic hash, forming a chain.
Consensus: The network reaches a consensus on the validity of the new block, and it is added to the blockchain.
Applications of Blockchain
Blockchain technology has the potential to disrupt various industries, including:
Finance: Blockchain can streamline financial transactions, reduce costs, and enhance security in the banking and payment sectors.
Healthcare: Blockchain can improve patient data security, streamline medical records, and facilitate secure data sharing between healthcare providers.
Supply Chain: Blockchain can enhance supply chain transparency, reduce fraud, and improve efficiency in tracking goods and services.
Real Estate: Blockchain can simplify property transactions, reduce costs, and increase security in the real estate market.
Government: Blockchain can improve transparency and accountability in government processes, such as voting and record-keeping.
Challenges and Limitations

While blockchain offers numerous benefits, it also faces several challenges and limitations:
Scalability: Blockchain networks can struggle to handle a large number of transactions simultaneously, leading to network congestion and slower processing times.
Energy Consumption: The process of mining new blocks requires significant computational power and energy, raising concerns about environmental impact.
Regulatory Hurdles: The evolving nature of blockchain technology presents regulatory challenges for governments and industries.
Security Concerns: Although blockchain is generally secure, vulnerabilities can still exist, and malicious actors may attempt to exploit these weaknesses.
Conclusion

Blockchain technology has the potential to revolutionize various industries by providing a secure, transparent, and efficient platform for data management and transactions. As the technology continues to evolve and overcome its challenges, its impact on society is expected to grow exponentially.
Tags: