大数据在英语中被称为 Big Data。它是指规模巨大、增长快速、类型多样的数据集合,这些数据集合通常难以用传统的数据处理工具进行有效管理。大数据的特点包括:
1. Volume(数量):数据量非常大,通常以TB或PB为单位。2. Velocity(速度):数据产生和处理的速率非常快。3. Variety(多样性):数据类型多样,包括结构化、半结构化和非结构化数据。4. Veracity(真实性):数据的质量和准确性。5. Value(价值):数据中蕴含着有价值的信息和洞察。
大数据分析技术可以帮助企业从这些数据中提取有价值的信息,以支持决策制定、优化业务流程、提高客户满意度等。
Introduction to Big Data
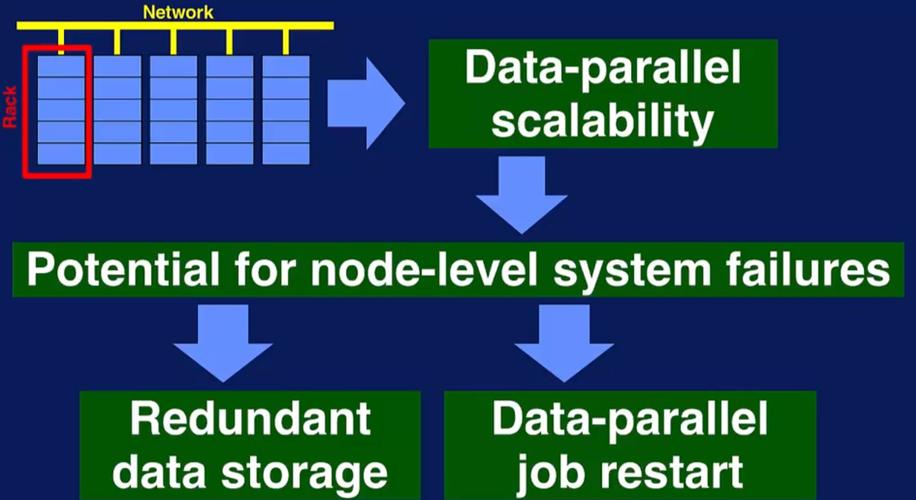
Big data has emerged as a pivotal force in the modern digital era, transforming the way businesses, governments, and individuals operate. This article delves into the concept of big data, its characteristics, applications, and the technologies that power this data revolution.
What is Big Data?

Big data refers to vast and complex data sets that are too large and complex to be processed using traditional data processing applications. These data sets are characterized by the 4Vs: Volume, Variety, Velocity, and Veracity.
Volume: The sheer size of big data is massive, often measured in terabytes, petabytes, or even exabytes.
Variety: Big data encompasses a wide range of data types, including structured, semi-structured, and unstructured data.
Velocity: Data is generated and processed at an unprecedented speed, requiring real-time or near-real-time analysis.
Veracity: The quality and reliability of big data can vary significantly, making it challenging to extract meaningful insights.
Characteristics of Big Data

Understanding the characteristics of big data is crucial for harnessing its potential. Here are some key aspects:
High Volume: Big data is characterized by its massive size, which can overwhelm traditional data processing systems.
High Velocity: Data is generated and processed at an incredible speed, requiring real-time or near-real-time analysis to derive actionable insights.
High Variety: Big data encompasses a wide range of data types, including structured, semi-structured, and unstructured data, making it challenging to process and analyze.
High Veracity: The quality and reliability of big data can vary significantly, requiring careful data cleaning and preprocessing.
Applications of Big Data
Big data has a wide range of applications across various industries, including:
Healthcare: Big data analytics can help in improving patient care, identifying disease patterns, and optimizing treatment plans.
Finance: Financial institutions use big data to detect fraudulent transactions, manage risks, and personalize financial services.
Marketing: Companies leverage big data to gain insights into customer preferences, optimize marketing campaigns, and improve customer satisfaction.
Government: Governments use big data to improve public services, enhance public safety, and make informed policy decisions.
Technologies for Big Data
Several technologies enable the processing, storage, and analysis of big data. Here are some key technologies:
Hadoop: An open-source framework for distributed storage and processing of big data.
NoSQL Databases: Non-relational databases designed to handle large volumes of data and provide high scalability.
Spark: An open-source, distributed computing system that provides fast and general-purpose data processing.
Challenges and Opportunities in Big Data

While big data offers immense opportunities, it also presents several challenges:
Data Privacy: Ensuring the privacy and security of sensitive data is a significant concern.
Data Quality: Ensuring the accuracy and reliability of big data is crucial for making informed decisions.
Data Integration: Integrating data from various sources can be complex and time-consuming.
Skilled Workforce: There is a growing demand for skilled professionals who can work with big data technologies.
Despite these challenges, the potential of big data is immense, and organizations that can effectively harness its power will gain a competitive edge in the digital age.
Conclusion
Big data has become an indispensable part of our lives, offering unprecedented opportunities for innovation and improvement. By understanding its characteristics, applications, and the technologies that power it, we can better navigate the big data landscape and unlock its full potential.