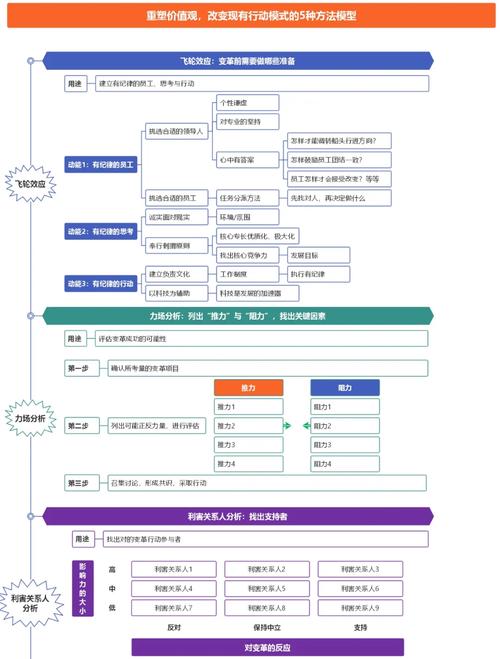
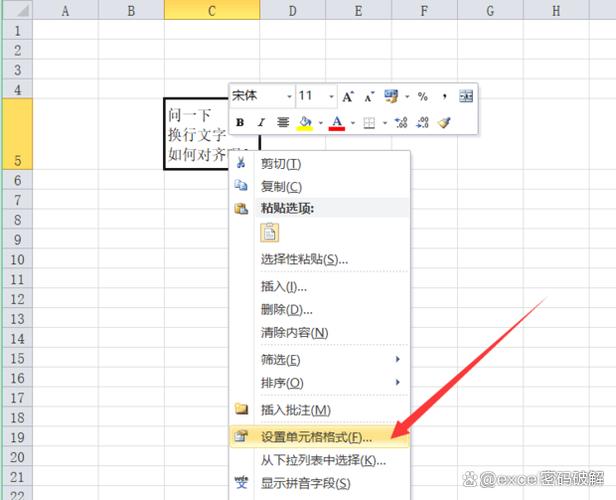
大数据的英文是 Big Data。
Introduction to Big Data
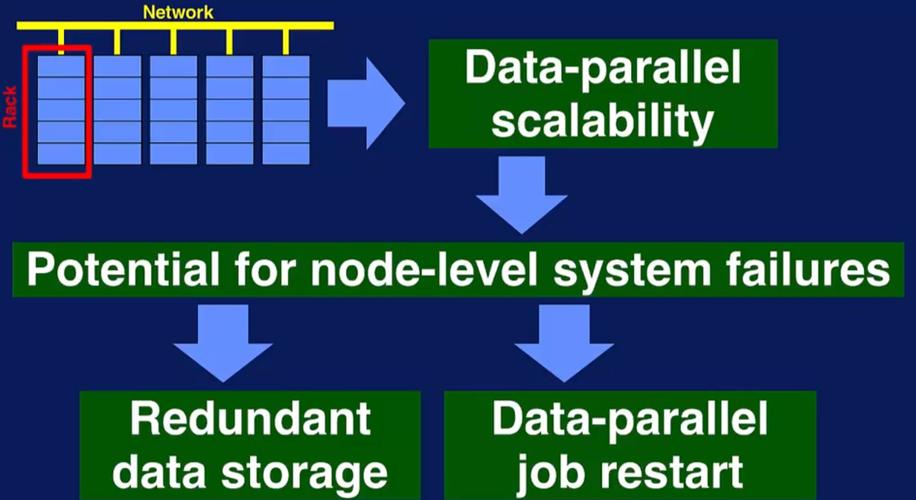
Big Data has emerged as a pivotal force in the modern digital era, transforming how businesses, governments, and individuals operate. This article delves into the concept of Big Data, its significance, and its applications across various sectors.
What is Big Data?

Big Data refers to vast and complex data sets that are too large and complex to be processed using traditional data processing applications. These datasets are characterized by their volume, velocity, and variety. The three V's of Big Data—volume, velocity, and variety—define its unique nature and the challenges it poses for data management and analysis.
Volume: The Exponential Growth of Data
Volume is the sheer size of the data. With the advent of the internet, social media, and IoT devices, the amount of data generated has been skyrocketing. According to IDC, the global data volume is expected to reach 175 zettabytes by 2025. This exponential growth necessitates the development of new technologies and methodologies to store, manage, and analyze such vast amounts of data.
Velocity: The Speed at Which Data is Generated and Processed
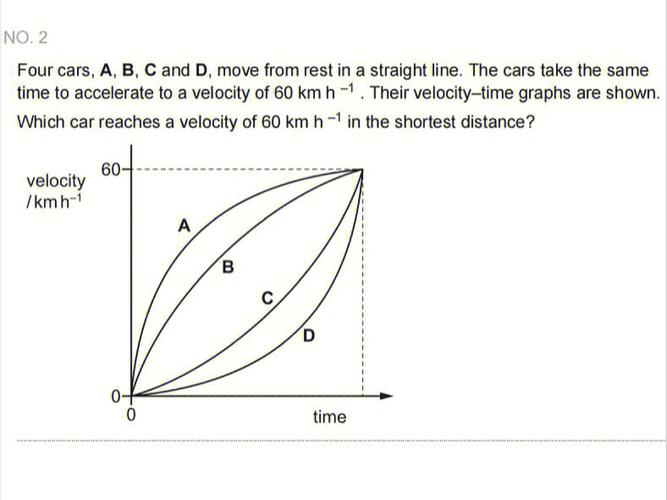
Velocity refers to the speed at which data is generated, collected, and processed. In today's fast-paced world, real-time data processing is crucial for making informed decisions. For instance, financial institutions use high-speed data processing to detect fraudulent transactions in real-time, while e-commerce platforms leverage real-time analytics to personalize user experiences.
Variety: The Diverse Types of Data

Variety encompasses the different types of data, including structured, semi-structured, and unstructured data. Structured data is organized and stored in a predefined format, such as relational databases. Semi-structured data has some organization but does not conform to a rigid schema, while unstructured data is completely unorganized, like text, images, and videos. The diverse nature of Big Data requires advanced analytics techniques to extract meaningful insights.
Big Data Technologies
Several technologies have been developed to address the challenges posed by Big Data. Some of the key technologies include:
Hadoop
Hadoop is an open-source framework that allows for the distributed storage and processing of large data sets across clusters of computers. It is designed to scale up from single servers to thousands of machines, each offering local computation and storage.
MapReduce
NoSQL Databases
NoSQL databases are designed to store and manage large volumes of unstructured data. They offer high scalability, flexibility, and performance, making them ideal for Big Data applications.
Applications of Big Data

Big Data has a wide range of applications across various sectors:
Healthcare
Big Data analytics in healthcare can lead to improved patient outcomes, better disease management, and personalized medicine. By analyzing large volumes of patient data, healthcare providers can identify patterns and trends that can help in early detection and treatment of diseases.
Finance
Financial institutions use Big Data to detect fraudulent transactions, manage risks, and personalize financial services. Real-time analytics enable banks to make informed decisions and offer tailored products to their customers.
Marketing
Big Data analytics in marketing helps businesses understand consumer behavior, optimize marketing campaigns, and improve customer satisfaction. By analyzing customer data, companies can identify trends and preferences, leading to more effective marketing strategies.
Government
Big Data can be used by governments to improve public services, enhance public safety, and make informed policy decisions. For instance, analyzing traffic data can help in optimizing traffic flow and reducing congestion.
Conclusion
Big Data has become an indispensable part of our lives, offering immense potential for innovation and improvement across various sectors. As the volume, velocity, and variety of data continue to grow, it is crucial for organizations to embrace Big Data technologies and analytics to stay competitive and make data-driven decisions.